SMART options and signs of a hard drive failure
Read about the SMART hard drive options that warn about device wear or malfunction . System SMART (or SMART) was developed by hard disk drive manufacturers in order to unify access to disk system information regarding its reliability and performance. The numerous parameters available through the SMART system make it possible to determine the signs of an early disk failure at an early stage. At the same time, the number of available parameters is so large that it is not easy to obtain any useful information from them. 
This article discusses the most important parameters of SMART, a correct understanding of which will allow you to learn about the imminent hard disk failure, replace a worn device in time and avoid the need for recover deleted information .
Content:
- Tools.
- SMART options
Tools
Many hard drive manufacturers (for example, AData, PQI, Transcend) offer their own tools that interpret the data provided by the SMART system. On the one hand, using such tools is easy and convenient: they provide a clear and unambiguous assessment of the condition of the disk. Programs from manufacturers know how to correctly interpret data from a variable (as we will see below, it is not so easy to do). On the other hand, the information provided by such tools is often not enough for thoughtful analysis, and assessments based on unknown data processed by unknown algorithms should not be trusted unconditionally.
Alternatively, third-party tools like the free CrystalDiskInfo . The program is as follows (by the way, it provides the ability to switch to Russian):
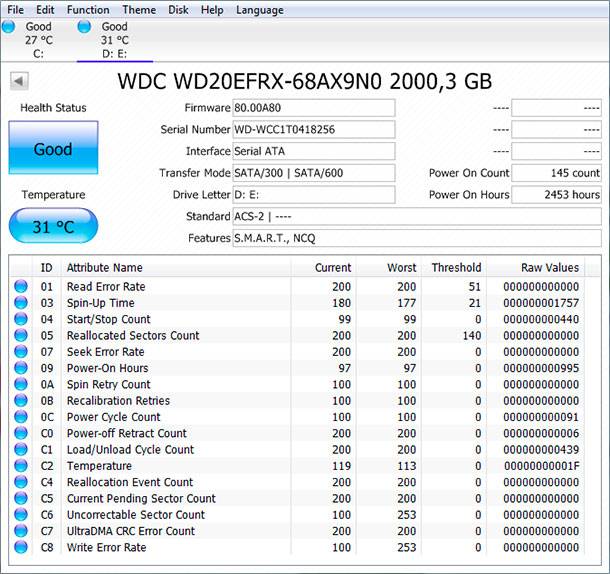
SMART options
Let's take a closer look at the WD 2Tb hard drive. So, we see a list of many options. What should I look for in terms of disk reliability?
Let's see how the SMART program calculates the device reliability index. For hard drives, the program keeps track of parameters such as Reallocated Sectors Count , Current Pending Sectors Count and Uncorrectable Sector Count .
- Reallocated Sectors Count . This parameter keeps track of the number of unreliable and bad sectors forwarded by the disk controller to a special backup area. On quality new drives, this parameter should be zero, but sometimes there are instances with a non-zero counter value right out of the box. The mere existence of a small number (i.e., far below the threshold determined by the manufacturer) of such sectors is not a sign of a serious threat to the integrity of your data, but a gradual (and even more so rapid) increase in the number of displaced sectors indicates excessive or premature plate wear. disc, and is a direct indication for replacing such a disc.
- Marked to redirect sector (English Current Pending Sector Count ). Hard disk manufacturers interpret this parameter differently; in some models, tagged sectors may be considered valid for further use. In other models, such sectors eventually go into the "displaced" mode. In any case, the large value of this counter indicates the need to replace the disk, and its growth over time indicates the need for an urgent replacement.
- Bad sectors (English Uncorrectable Sector Count ). If the data cannot be read after many attempts, it is meaningless to move such a sector - it is marked as failed. The presence of a significant number of such sectors is a sign of wear or disc malfunction.
- Read errors (English Read Error Rate ). This parameter is interpreted differently by different manufacturers, so its analysis is best left to the programs from the disk manufacturer.
- Write errors (English Write Error Rate ). This parameter is also interpreted differently by different manufacturers, so its analysis should also be left to the programs from the disc manufacturer.
- Forwarding events (eng. Reallocation Event Count ). The value of the variable increases with each successful or unsuccessful sector redirection. If the value of this counter increases with time - this is a direct indication that the disc is gradually wearing out.
- Attempts to spin the plates (English Spin Retry Count ). If the disk motor fails to spin the plates on the first attempt, the value of this counter increases. A noticeable number of such attempts indicates a high probability of mechanical failure of the disk.